
Type Index Pages
- BillboardGui
- CanvasGroup
- Frame
- Hint
- ImageButton
- ImageLabel
- PlayerGui
- ScreenGui
- ScrollingFrame
- StarterGui
- SurfaceGui
- TextBox
- TextButton
- TextLabel
- UIAspectRatioConstraint
- UIGradient
- UIGridLayout
- UIListLayout
- UIPadding
- UIPageLayout
- UIScale
- UISizeConstraint
- UITableLayout
- UITextSizeConstraint
- VideoFrame
- ViewportFrame
- ChangeHistoryService
- CoreGui
- DataModelSession
- DockWidgetPluginGui
- MultipleDocumentInterfaceInstance
- Plugin
- PluginAction
- PluginGui
- PluginGuiService
- PluginManager
- PluginMenu
- PluginMouse
- PluginToolbar
- PluginToolbarButton
- QWidgetPluginGui
- Selection
- StandalonePluginScripts
- StatsItem
- StudioService
- StudioTheme
No results found!
-
Instance
- GameSettings
- DebugSettings
- BodyMover
- WeldConstraint
- HttpRbxApiService
- NotificationService
- Translator
- Lighting
- Beam
- GuiService
- UserInputService
- Studio
- Plugin
- HttpService
- Mouse
- BindableEvent
- RunService
- Pages
- Humanoid
- TestService
- PathfindingService
- Chat
- NetworkPeer
- Feature
- CharacterAppearance
- Constraint
- NetworkReplicator
- JointInstance
- Light
- BasePlayerGui
- AnalyticsService
- NetworkMarker
- BinaryStringValue
- FlyweightService
- Geometry
- LoginService
- InstancePacketCache
- ThirdPartyUserService
- TouchInputService
- RuntimeScriptService
- GuidRegistryService
- PartOperationAsset
- DialogChoice
- PhysicsService
- AdService
- TextService
- MarketplaceService
- TeleportService
- Accoutrement
- GamePassService
- AssetService
- InsertService
- PointsService
- ChangeHistoryService
- ServerScriptService
- JointsService
- LogService
- InputObject
- Toolbar
- LuaSettings
- RenderSettings
- AnimationTrack
- PhysicsSettings
- NetworkSettings
- CFrameValue
- Animation
- Color3Value
- BoolValue
- BrickColorValue
- Vector3Value
- AnimationController
- BindableFunction
- Button
- Trail
- LocalizationTable
- LocalizationService
- DebuggerBreakpoint
- DebuggerWatch
- ScriptDebugger
- Animator
- Attachment
- RemoteFunction
- RemoteEvent
- PluginManager
- Camera
- Stats
- Sky
- StarterPlayer
- Dragger
- TerrainRegion
- Path
- TextFilterResult
- Dialog
- StatsItem
- GoogleAnalyticsConfiguration
- ScriptContext
- ControllerService
- CacheableContentProvider
- ReflectionMetadataClasses
- ReflectionMetadataEnums
- DebuggerManager
- GuiBase
- UIBase
- LuaSourceContainer
- GuiItem
- DataModelMesh
- ServiceProvider
- ReflectionMetadataItem
- PostEffect
- PhysicsPacketCache
- TouchTransmitter
- RobloxReplicatedStorage
- Visit
- LuaWebService
- ScriptService
- FlagStandService
- VirtualUser
- SpawnerService
- TimerService
- CookiesService
- Team
- GroupService
- StarterGear
- Message
- PlayerScripts
- Configuration
- ContentProvider
- CollectionService
- Debris
- ReplicatedFirst
- ServerStorage
- ReplicatedStorage
- Folder
- TweenService
- Players
- ContextActionService
- StarterPlayerScripts
- SoundService
- KeyframeSequenceProvider
- VRService
- PluginGuiService
- Player
- Teams
- Pose
- Keyframe
- KeyframeSequence
- IntConstrainedValue
- DoubleConstrainedValue
- ForceField
- RayValue
- Fire
- Smoke
- Sparkles
- ParticleEmitter
- IntValue
- StringValue
- NumberValue
- Explosion
- ObjectValue
- SoundGroup
- UserGameSettings
- ClickDetector
- Sound
- Selection
- BadgeService
- TaskScheduler
- GlobalDataStore
- DataStoreService
- CustomEvent
- CustomEventReceiver
- VirtualInputManager
- FunctionalTest
- TweenBase
- SoundEffect
- ReflectionMetadataEvents
- ClusterPacketCache
- PVInstance
- FaceInstance
- Controller
- ReflectionMetadataCallbacks
- ReflectionMetadataFunctions
- ReflectionMetadataYieldFunctions
- ReflectionMetadataProperties
- ReflectionMetadata
- AdvancedDragger
- HapticService
- FriendService
- GamepadService
No Result Found !!!
NumberSequence
NumberSequence
A NumberSequence represents a series of number values from 0 to 1. The number values are expressed using the datatype/NumberSequenceKeypoint type. This type is used in properties of ParticleEmitter to indicate properties of particles over their lifetime. In Studio, this data type is edited using a line graph:
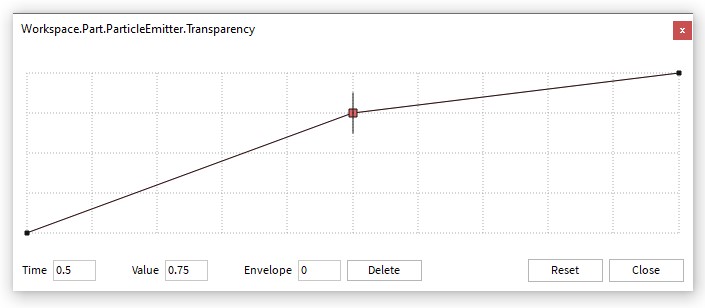
The above line graph can be set using a script using the following call to NumberSequence.new:
particleEmitter.Transparency = NumberSequence.new{
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(0, 0), -- (time, value)
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(.5, .75),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(1, 1)
}
Equality
Two NumberSequences are equivalent if and only if the values of their datatype/NumberSequenceKeypoint are equivalent, even if the two NumberSequence would result in similar graphs.
Evaluation
The NumberSequence type does not have a built-in method for getting the value at a certain time/point because keypoints can have random envelopes. Assuming the envelope values of your keypoints are all 0, you can use the following function to evaluate at a specific time:
function evalNS(ns, time) -- If we are at 0 or 1, return the first or last value respectively if time == 0 then return ns.Keypoints[1].Value end if time == 1 then return ns.Keypoints[#ns.Keypoints].Value end -- Step through each sequential pair of keypoints and see if alpha -- lies between the points' time values. for i = 1, #ns.Keypoints - 1 do local this = ns.Keypoints[i] local next = ns.Keypoints[i + 1] if time >= this.Time and time < next.Time then -- Calculate how far alpha lies between the points local alpha = (time - this.Time) / (next.Time - this.Time) -- Evaluate the real value between the points using alpha return (next.Value - this.Value) * alpha + this.Value end end end
You can use the function above like this:
local ns = NumberSequence.new{
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(0, 0),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(.5, .8),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(1, 1),
}
print(evalNS(ns, 0)) --> 0
print(evalNS(ns, .25)) --> .4
print(evalNS(ns, .5)) --> .8
print(evalNS(ns, .75)) --> .9
print(evalNS(ns, 1)) --> 1
Constructors
| NumberSequence.new ( number n ) |
|
Creates a sequence of two keypoints with local ns = NumberSequence.new(n)
-- is equivalent to
local ns = NumberSequence.new{
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(0, n),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(1, n),
}
|
| NumberSequence.new ( number n0, number n1 ) |
|
Creates a sequence of two keypoints with local ns = NumberSequence.new(n0, n1)
-- is equivalent to
local ns = NumberSequence.new{
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(0, n0),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(1, n1),
}
|
| NumberSequence.new ( table Keypoints ) |
|
Create a sequence given an array of local ns = NumberSequence.new{
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(0, 0),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(.5, .5, .25),
NumberSequenceKeypoint.new(1, 1),
}
|
Properties
| array NumberSequence.Keypoints |
|
An array containing keypoint values for the NumberSequence. |
How this site use cookies
This Platform uses cookies to offer you a better experience, to personalize content, to provide social media features and to analyse the traffic on our site. For further information, including information on how to prevent or manage the use of cookies on this Platform, please refer to our Privacy and Cookie Policy.